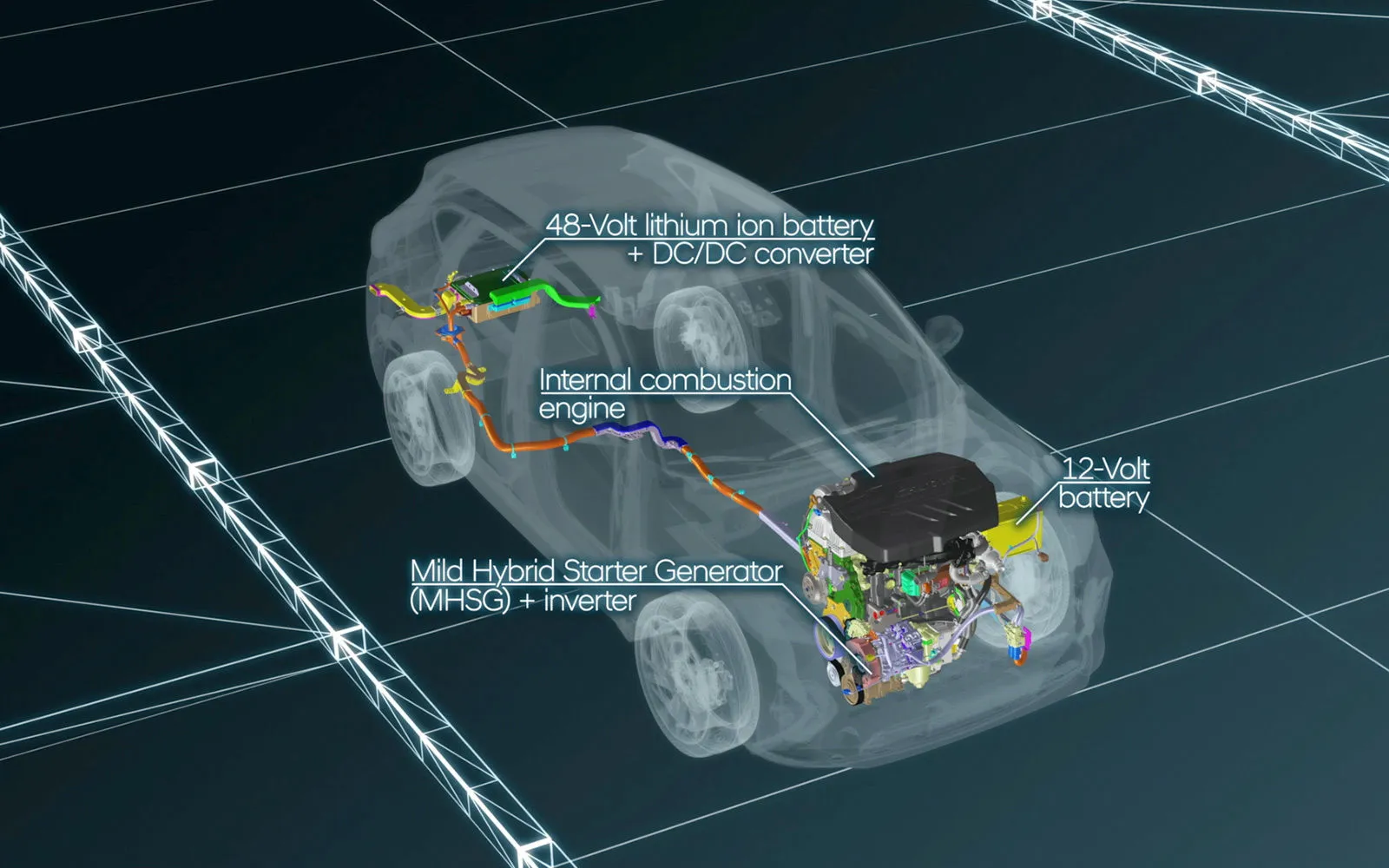
Hybrid batteries are designed very differently from consumer electronics batteries. They are engineered for durability, safety, and long-term integration with the vehicle’s powertrain. Understanding how hybrid battery technology works helps clarify common concerns and provides a more realistic picture of what ownership involves over time.
Hybrid Battery Technology and Design
Purpose of the Hybrid Battery System
The hybrid battery serves as an energy storage unit that supports the electric motor. It stores electricity generated through regenerative braking and, in some designs, from the gasoline engine itself. This stored energy is then used to assist acceleration, power low-speed driving, and reduce fuel consumption during inefficient engine operating conditions.
Unlike fully electric vehicles, hybrid batteries are not intended to power the vehicle for long uninterrupted distances. Instead, they operate within a controlled range that prioritizes efficiency and longevity. This design philosophy reduces stress on the battery and allows it to perform consistently across many driving cycles.
The battery works in constant coordination with the engine, motor, and control software. This system-level integration is a key reason why hybrid batteries behave differently from standalone battery systems.
Lithium-Ion Packs and Modern Chemistry
Most modern hybrid vehicles use lithium-ion battery packs. This chemistry offers advantages in energy density, responsiveness, and weight compared to older battery types. Lithium-ion packs are well suited to the frequent charging and discharging cycles that hybrids experience during everyday driving.
Hybrid lithium-ion batteries are optimized for partial charge operation rather than full discharge. This controlled usage pattern helps limit degradation and supports long-term reliability. The battery management system carefully monitors voltage, temperature, and usage patterns to keep the pack operating within safe limits.
The design of lithium-ion packs in hybrids prioritizes stability and durability over maximum range. This conservative approach aligns with the hybrid’s role as an efficiency-enhancing system rather than a primary energy source.
Battery Lifespan and Long-Term Performance
What Determines Battery Lifespan
Battery lifespan in hybrid vehicles depends on several interacting factors. Thermal stability, charge management, driving conditions, and overall system design all influence how the battery ages over time. Unlike consumer devices that may be fully charged and drained frequently, hybrid batteries operate within a narrower and more controlled range.
Driving style also plays a role. Smooth driving with gradual acceleration allows the battery to cycle more gently, while aggressive driving can increase energy flow and heat generation. However, the vehicle’s control system actively manages these factors to minimize unnecessary stress.
Because hybrid batteries are never pushed to their extremes, their usable life is often longer than many drivers initially expect.
Gradual Changes Rather Than Sudden Failure
Hybrid batteries typically do not fail suddenly. Instead, they experience gradual changes in performance over extended use. The vehicle’s management system is designed to adapt to these changes, maintaining consistent operation even as the battery ages.
As capacity slowly changes, the system adjusts how energy is used and stored. This means that most drivers do not notice abrupt differences in vehicle behavior. Warning systems and diagnostics are also built in to alert drivers if attention is required.
This gradual aging process contributes to the perception of reliability that many long-term hybrid owners report.
Thermal Management and System Protection
Why Temperature Control Matters
Temperature is one of the most important factors affecting battery health. Excessive heat or cold can accelerate wear and reduce efficiency. Hybrid vehicles use dedicated thermal management systems to regulate battery temperature during operation.
These systems may use air cooling, liquid cooling, or a combination of both, depending on the vehicle’s design. Sensors continuously monitor battery temperature and adjust cooling strategies as needed to maintain stable conditions.
Effective thermal management helps ensure consistent performance across different climates, whether the vehicle is operating in hot summers or cold winters.
Integration With Vehicle Controls
Thermal management is closely integrated with the vehicle’s overall control system. When conditions demand it, the vehicle may limit battery output or adjust power distribution to protect the battery. These adjustments are typically seamless and unnoticed by the driver.
This integrated approach reduces the likelihood of overheating and helps maintain long-term battery reliability. It also allows the vehicle to adapt to varying driving conditions without requiring manual intervention.
Replacement Cost and Ownership Considerations
Understanding Replacement Scenarios
Battery replacement is a topic that often raises concern among potential hybrid buyers. While hybrid batteries are durable, replacement may eventually be necessary under certain conditions. When replacement does occur, it is typically the result of long-term wear rather than unexpected failure.
Replacement cost can vary depending on vehicle design, battery size, and availability of parts. However, replacement is not a routine maintenance item and is generally considered a long-term ownership consideration rather than a frequent expense.
In many cases, individual battery modules can be serviced or replaced rather than replacing the entire pack, depending on the design and service approach.
Balancing Cost With Efficiency Benefits
When evaluating replacement cost, it is important to consider the broader ownership picture. Hybrid vehicles often deliver reduced fuel consumption and smoother operation over time. These benefits contribute to overall value and can offset concerns about future battery service.
Advances in manufacturing and wider adoption of hybrid technology have also improved parts availability and service expertise. This has helped stabilize long-term ownership expectations for many drivers.
Warranty Coverage and Manufacturer Support
Typical Battery Warranty Practices
Hybrid batteries are commonly covered by extended warranty programs offered by manufacturers. These warranties reflect confidence in battery durability and provide reassurance to buyers concerned about long-term reliability.
Warranty coverage typically focuses on defects and performance issues rather than normal aging. This distinction ensures protection against unexpected problems while recognizing that gradual wear is a natural process.
Drivers should review warranty terms carefully, as coverage details may vary by manufacturer and region.
Role of Warranty in Consumer Confidence
Warranty coverage plays a significant role in shaping consumer trust in hybrid technology. Knowing that the most complex component of the vehicle is supported for an extended period reduces uncertainty and encourages adoption.
For many owners, warranty protection aligns with the typical duration of vehicle ownership, meaning battery concerns are unlikely to arise during that time. This contributes to the perception of hybrids as dependable long-term vehicles.
Reliability and Real-World Ownership Experience
Hybrid Battery Reliability in Daily Use
In real-world driving, hybrid batteries are designed to operate quietly and reliably in the background. Most drivers rarely think about the battery because it functions automatically as part of the overall powertrain.
Reliability comes from conservative design choices, continuous monitoring, and built-in safeguards. These factors work together to ensure stable operation across a wide range of driving conditions.
Hybrid battery systems are tested extensively to ensure they can handle repeated cycles, varying climates, and long-term use without compromising safety or performance.
Consumer Confidence Over Time
As hybrid vehicles have become more common, long-term ownership experiences have helped shape public understanding of battery reliability. Many drivers find that battery performance remains consistent throughout their ownership period.
This growing body of real-world experience has helped reduce early skepticism and has positioned hybrid battery technology as a mature and dependable solution rather than an experimental feature.
Questions and Answers
Q: How long do hybrid batteries typically last?
Hybrid batteries are designed for long-term use and gradual aging. They typically last for many years under normal driving conditions due to controlled charging and thermal management.
Q: Are lithium-ion batteries safe in hybrid vehicles?
Yes. Hybrid lithium-ion packs include extensive safety systems, monitoring, and thermal controls to ensure stable and safe operation.
Q: Is battery replacement common for hybrid owners?
Battery replacement is not common during typical ownership periods. When it does occur, it is usually after extended long-term use rather than sudden failure.
Q: Does warranty coverage apply to hybrid batteries?
Most manufacturers provide extended warranty coverage for hybrid batteries, offering protection against defects and unexpected issues.